Chapter 1
An Overview of Business Intelligence, Analytics, and Data Science.
1. Decision Support Systems (DSS)
- Decision support systems couple the intellectual resources of individuals with the capabilities of the computer to improve the quality of decisions.
- They use data, models, and sometimes knowledge management to find solutions for semistructured and unstructured problems.
Evolution of decision support systems:

2. Business Intelligence (BI)
The process of BI:
- Extract value from data (mainly through data mining).
- Add value to data (mainly through transformation and analytics).
Modern BI Mantra: Employees need the right information at the right time and in the right place.
Useful points:
- Many organizations employ descriptive analytics to replace their traditional flat reporting with interactive reporting that provides insights, trends, and patterns in the transactional data.
- BI tools need to be integrated amongst themselves, creating synergy.
- Service-oriented architecture, and software/infrastructure as a service are enablers of agile BI.
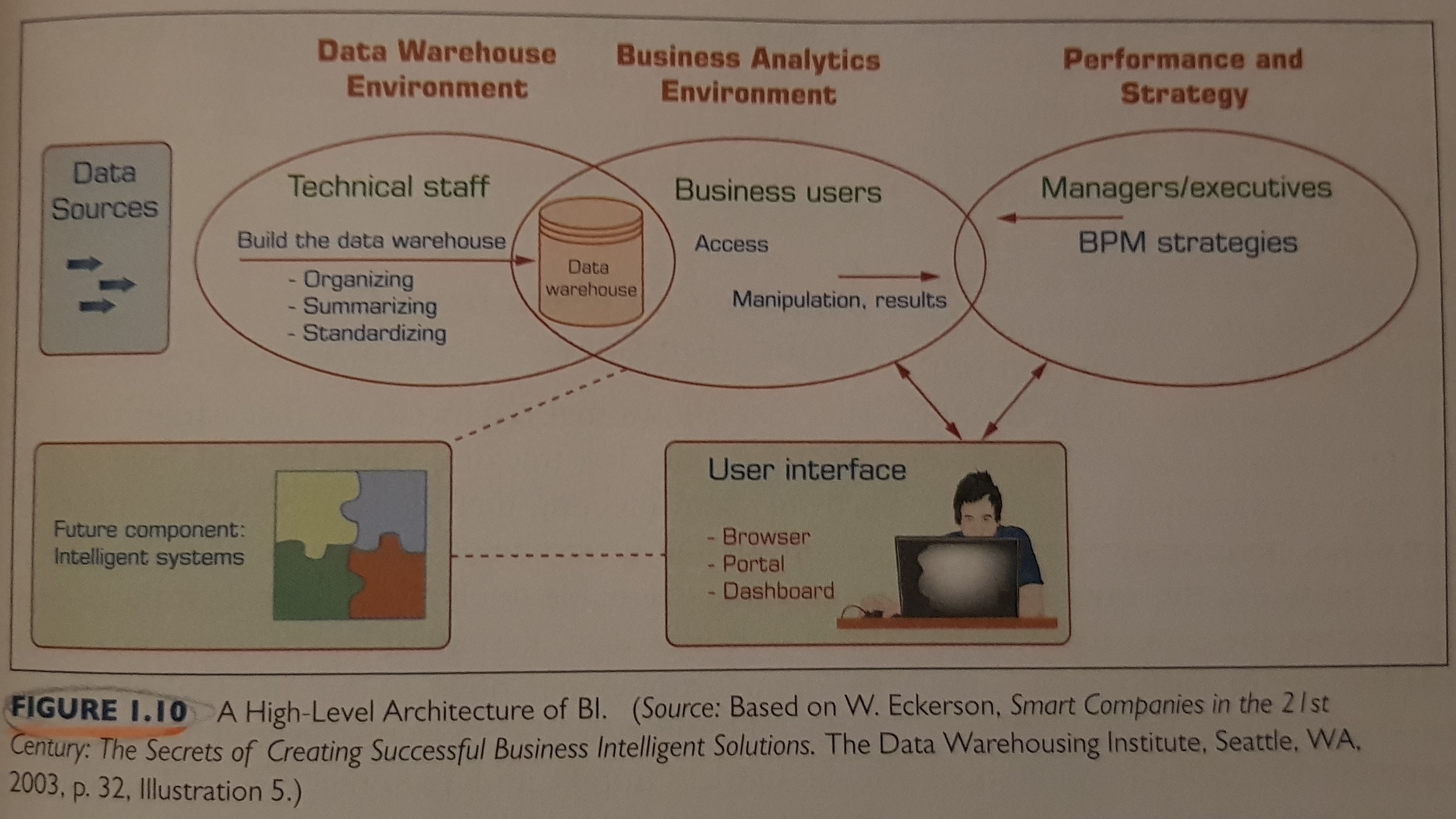
3. Data Warehouse (DW)
DW’s contain a wide variety of data that presents a coherent picture of business conditions at a single point in time. They also include historical data, but reorganized and structured in such a way that makes it fast and effecient for querying, analysis, and decision support.
Right-time data warehousing is better than real-time data warehousing, and when real-time data is needed you can either:
- Populate content into a DW in a manner that is faster than a typical ETL.
- Or Bypass the DW completely and provide content directly to end users. Example:
A vendor provides a new real-time dashboard. However the backend data takes time to be integrated into the DW and develop the necessary ETL. The solution here would be to allow the vendor to provide his new real-time dashboard, while simultaneously letting the data engineer work on developing the necessary pipeline to integrate the data into the DW. Once the data engineer is done, let the data analyst create a new dashbaord that can “synergize” with the data available in the DW, providing a higher value to end users and maintaining consistency with regards to how the data is defined across the organization.
4. Analytics
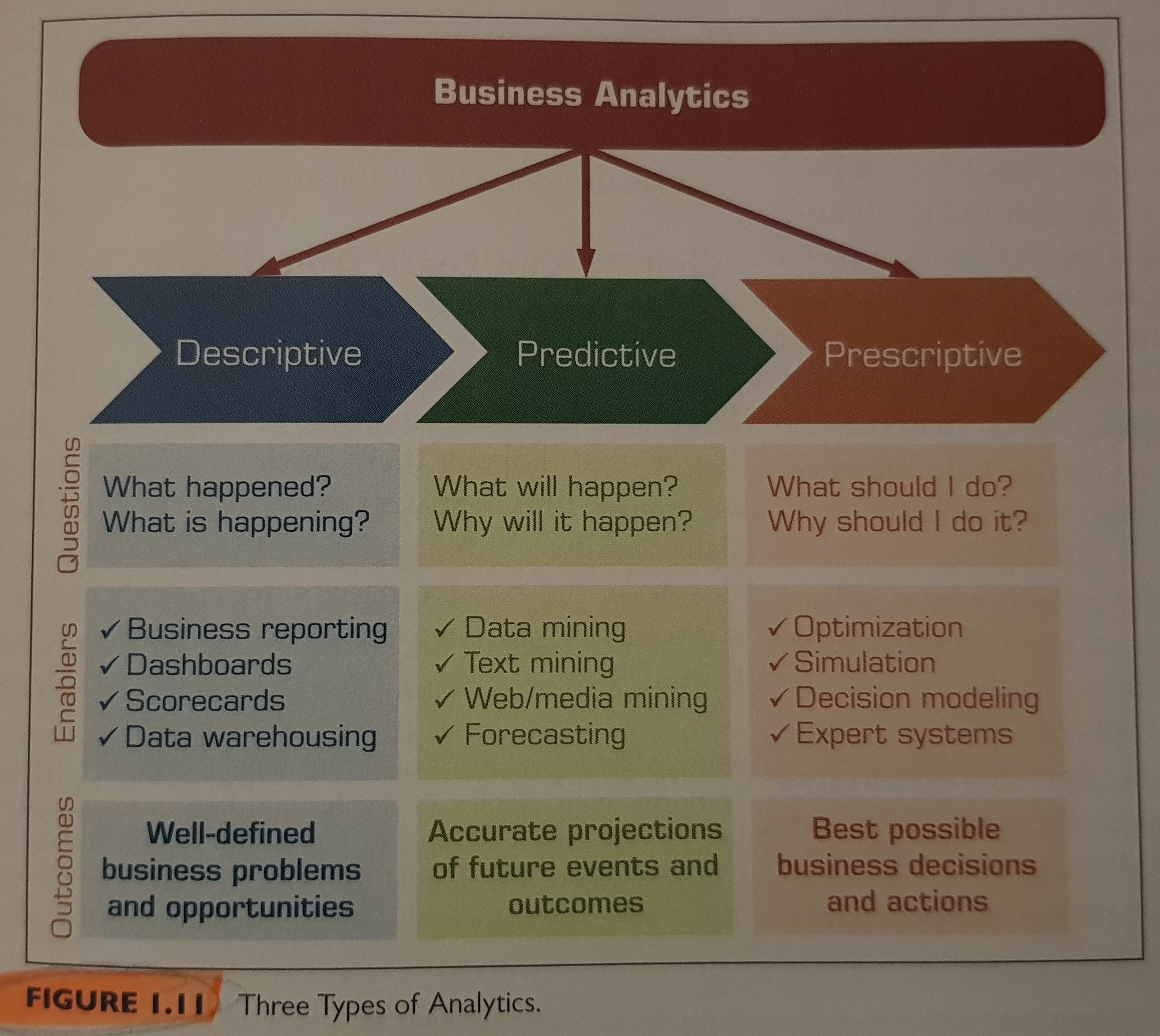
What is analytics? It is the process of developing actionable decisions or recommendations based on historical data, and they break into three major types:
Data Analytics vs. Data Science:
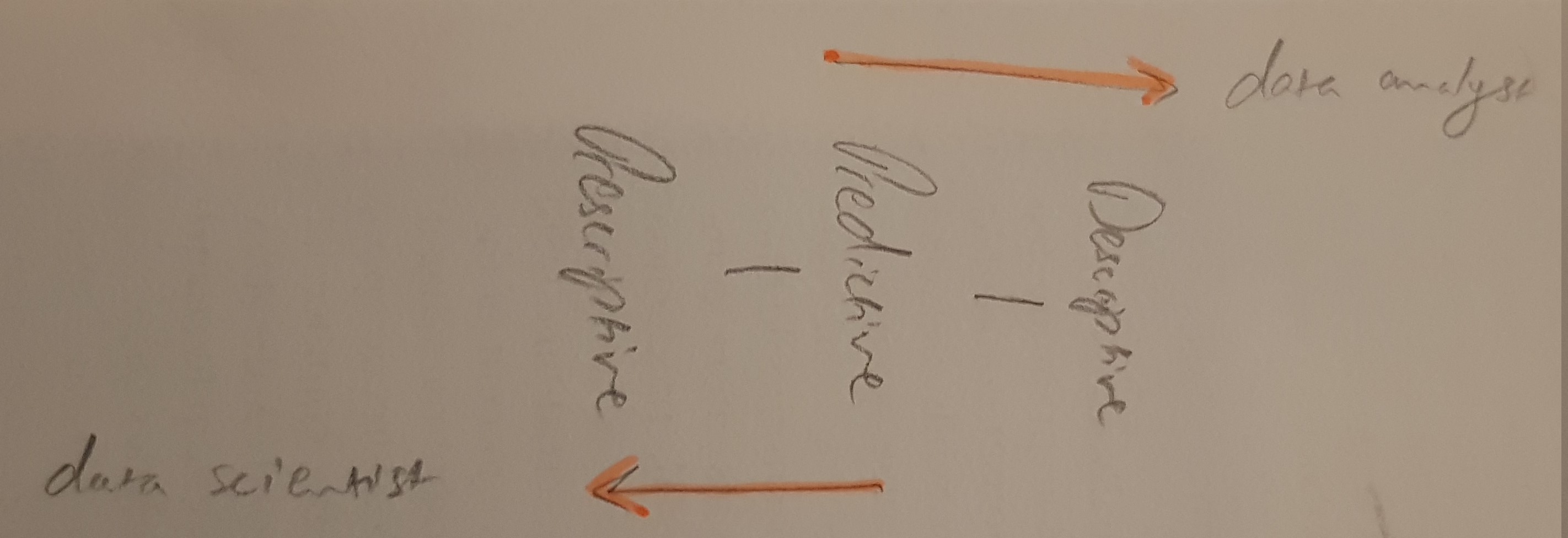
Examples of analytics applications in the retail value chain:

5. Big Data
Big data is any data that gives you trouble either with storage or processing.
Solutions?
- For storage, use HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System).
- For processing, push computation to the data instead of pushing data to a computation node, use Hadoop MapReduce.
The Big Data Landscape: provided by Matt Turck, a venture capitalist.