Chapter 8
Future Trends, Privacy and Managerial Considerations in Analytics.
1. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT infrastructure:
- hardware
- connectivity
- software backend
- applications
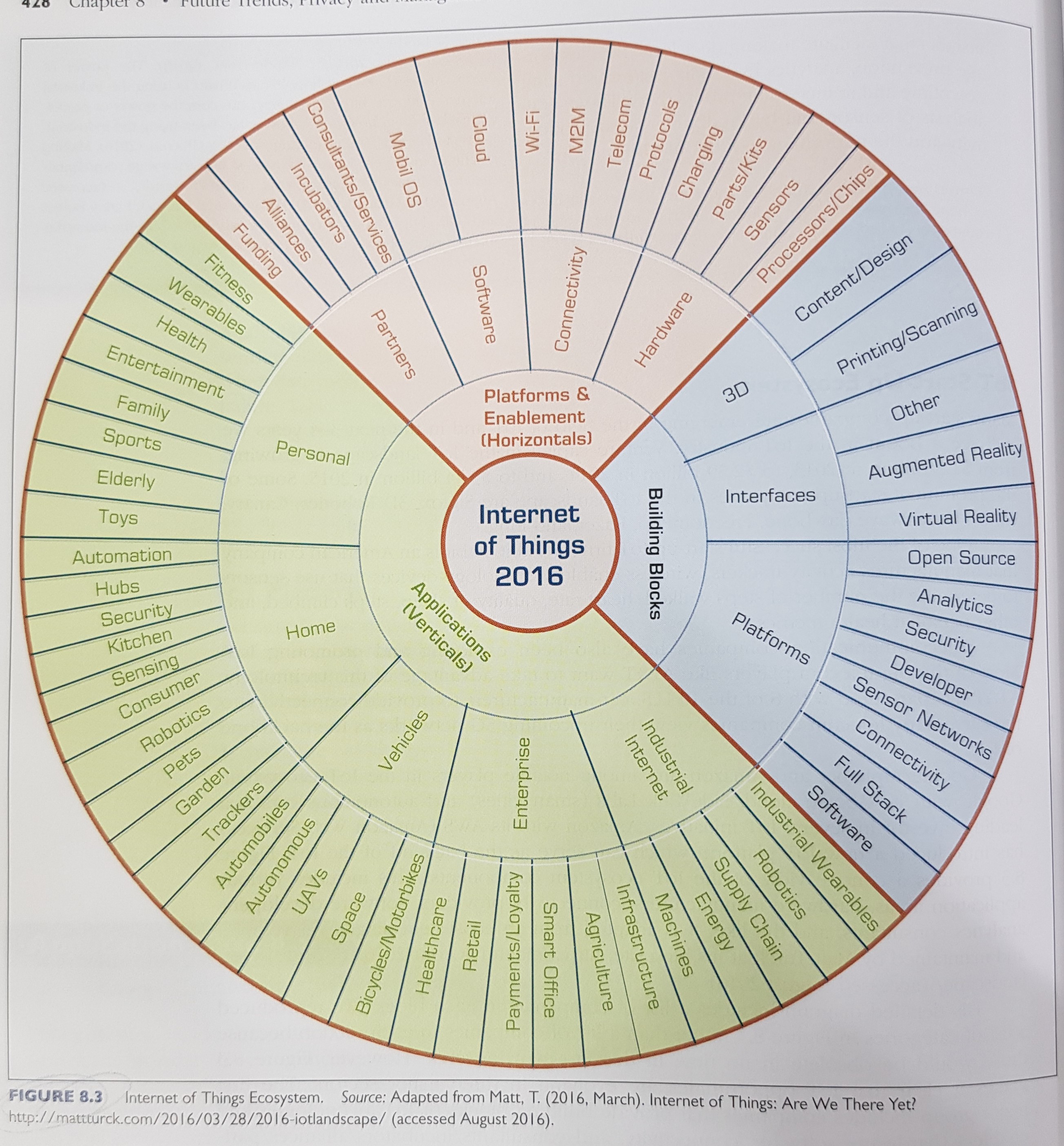
IoT ecosystem:
Managerial considerations in IoT:
- organizational alignment.
- interoperability challenges.
- security.
2. Fog Computing
- One of the key issues in IoT is that the data produced by sensors is huge, and not all of it is useful.
- So how much should be uploaded to the cloud servers for analysis?
- A recent concept to address this question is the idea of fog computing.
- Fog extends the cloud to be closer to the things that produce and act on IoT data.
- Analyzing data close to the devices minimizes latency and conserves bandwidth.
- Fog computing is crucial in situations when data needs to be analyzed in less than a second.
Fog vs. Cloud:

3. Cloud Computing
Cloud deployment models:
- private cloud
- public cloud
- hybrid cloud
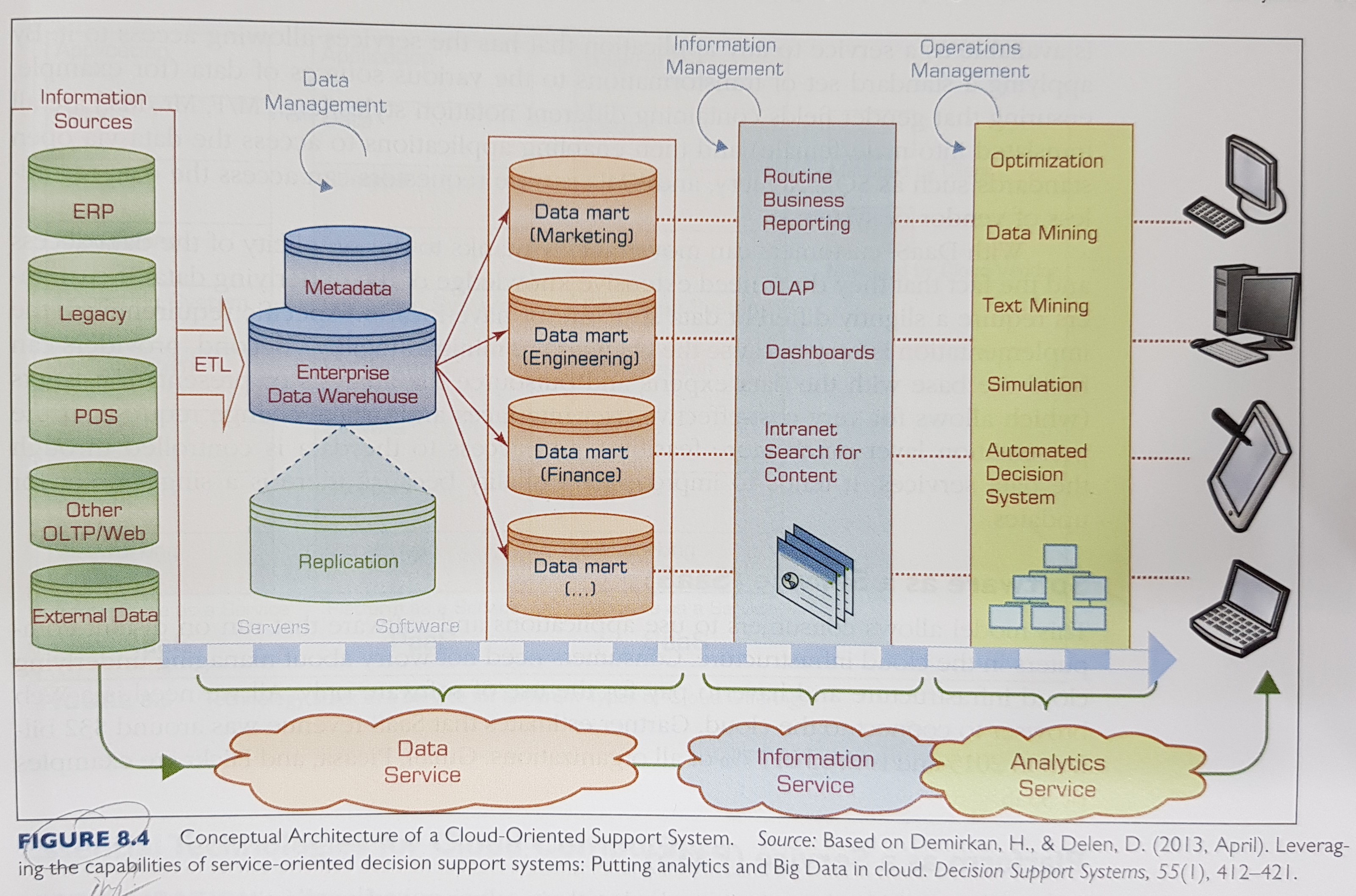
A mapping between current DW architecture and the cloud:
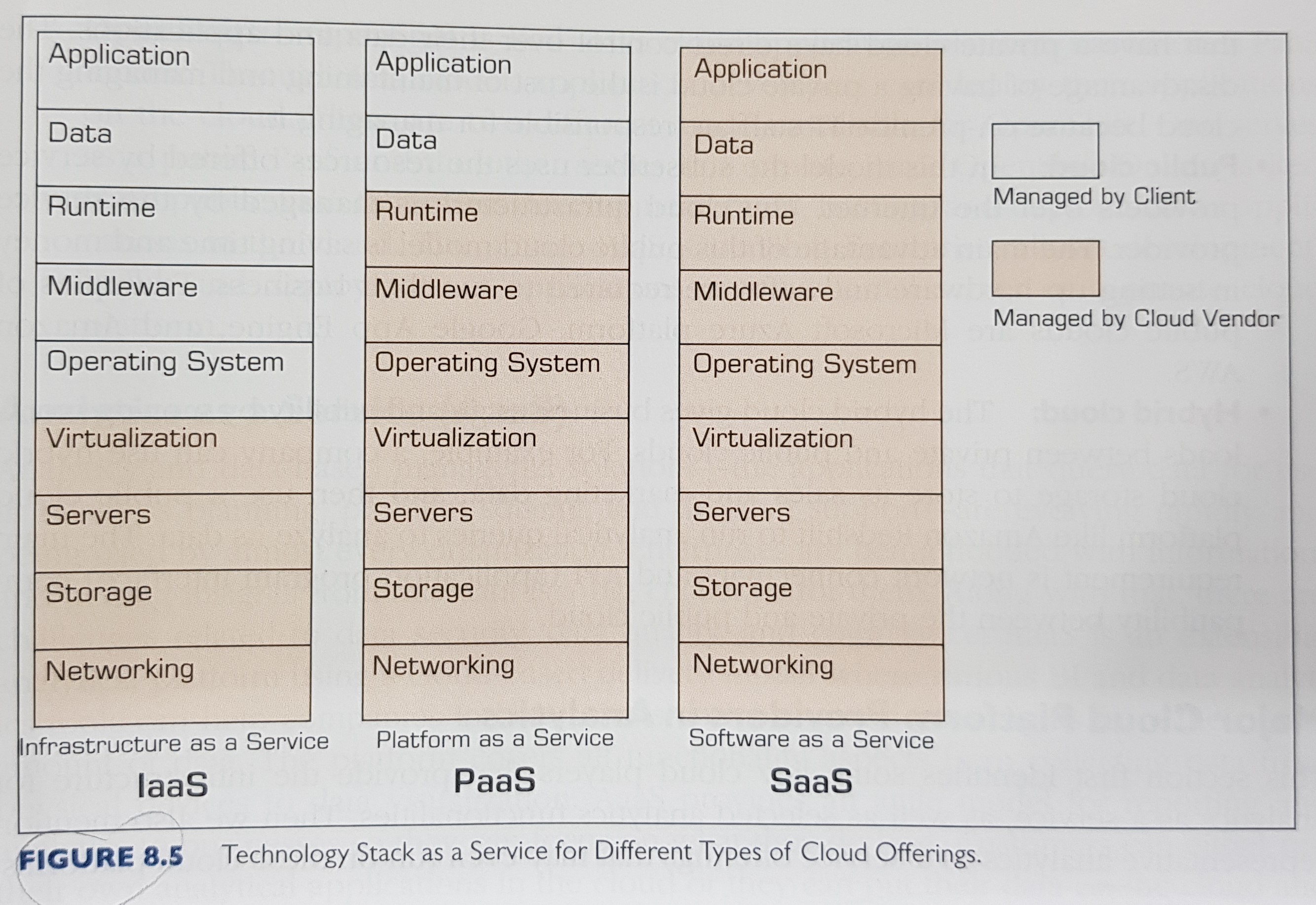
Technology stack as a service for different types of cloud offerings:
4. Technology Impact
Impact of analytics on managers:
- less importance of physical appearance.
- less expertise is required for making many decisions.
- faster decision making is possible.
- less reliance on experts and analysts – that is if the organization is analytics ready, and for preprocessed data only.
- power is being redistributed among managers – the more information and analysis capability they possess, the more power they have.
- automation of routine decisions may eliminate some managers.
Who is at risk?
- in general, it has been found that the job of middle managers is the most likely job to be automated.
- managers at lower levels do not spend much time on decision making. instead, they supervise, train, and motivate nonmanagers. some of their routine decisions, such as scheduling, can be automated; other decisions that involve behavioural aspects cannot.
- the job of top managers is the least routine and therefore the most difficult to automate.
Effect on organizations?
- because machines tend to be available at all hours and at all locations, an organization’s reach may increase, resulting in easier scaling and thus greater competition between organizations.
Bottom line?
- DS / AI automation of cognitive abilities will accelerate labor market “polarization”.
- significant job growth in top and bottom tiers in the job market.
- specialized knowledge that was applied over and over with some variation are at the greatest risk of disappearing.
- even if DS / AI does not replace workers directly, it will certainly require them to acquire new skills to remain competitive.
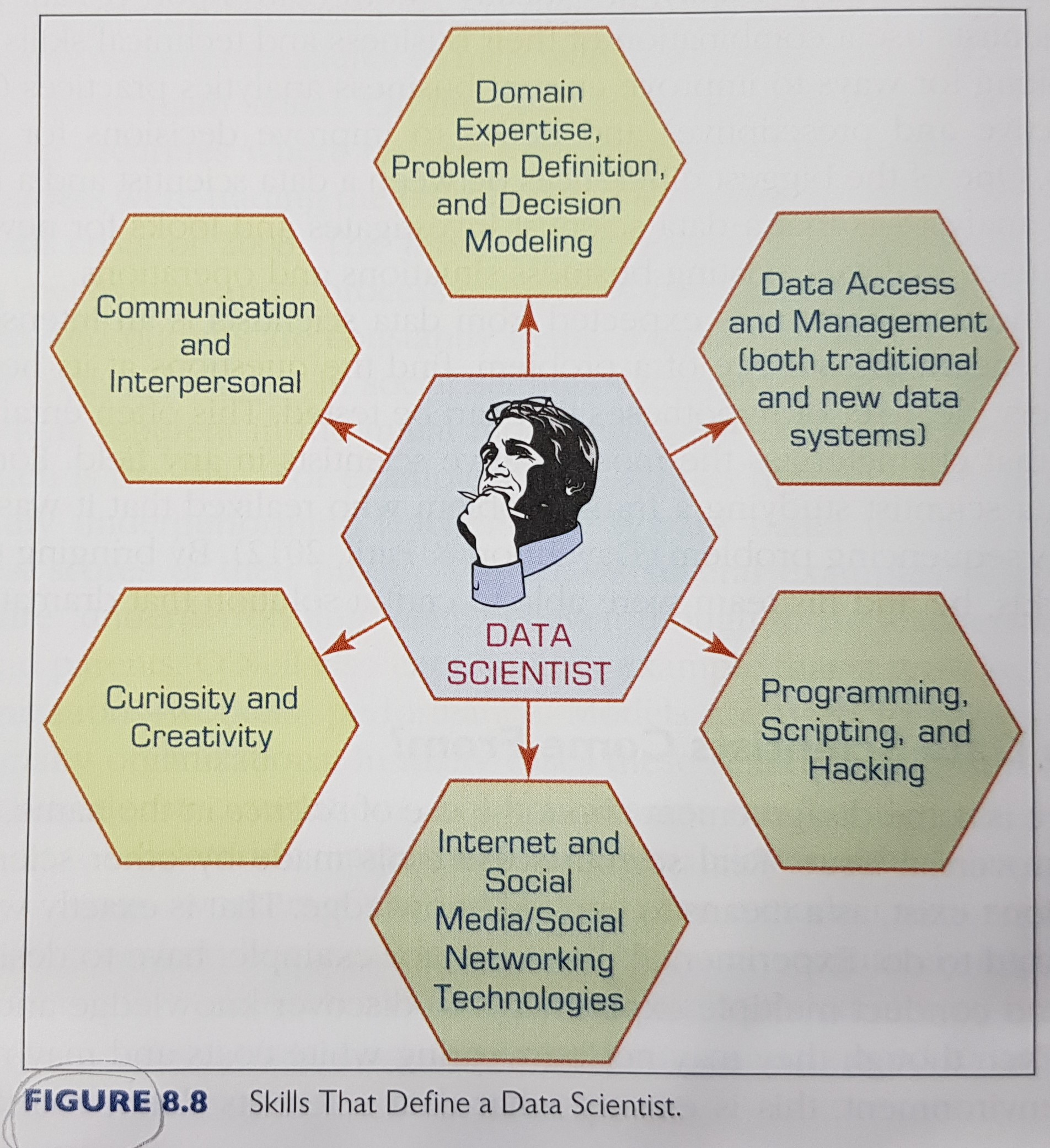
What are the skills that define a data scientist?