Git Summary
1. Overview
Sources used
- The missing semester Git lecture (made available by MIT).
- Pro Git book (freely available).
- Git manual.
Introduction
Git is a Distributed Version Control System (DVCS). It uses a directed acyclic graph (DAG) to model history (i.e., it supports branching):
o <-- o <-- o <-- o
^
\
--- o <-- oSnapshots are modeled as follows:
<root> (tree)
|
+- foo (tree)
| |
| + bar.txt (blob, contents = "hello world")
|
+- baz.txt (blob, contents = "git is wonderful")All snapshots are identified either by their SHA-1 hashes or their references (e.g., “master”).
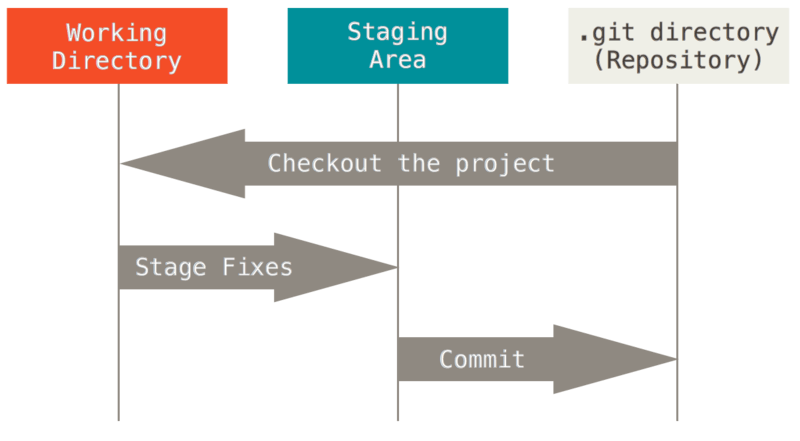
Git main areas
2. Essential Commands
Setting up Git
1. Install
$ sudo apt install git
2. Configure
$ git config --global user.name "your name" $ git config --global user.email "your email" $ git config --global core.editor "your favourite text editor"
3. Check configuration
$ git config --list
4. Help
$ git help [command]
Setting your repository
Option 1: Clone from an existing repository
# full clone $ git clone <URL ending with .git> # shallow clone $ git clone --depth=1 <URL ending with .git>
Option 2: Initialize your own repository
# initialize repo $ git init # specify which files / directories to ignore $ vim edit .gitignore # check log, current status, difference $ git log [--all --graph --decorate] $ git status $ git diff [filename] # stage files $ git add <filename, leading directory, or use --all> # commit changes $ git commit ####################################################### # Optional: linking to a remote server (such as github) ####################################################### # link to a remote repo and verify $ git remote add [-t branch] <name, usually called "origin"> <URL> $ git remote -v # push changes to remote repo $ git push <remote name, normally "origin"> <local branch, normally "master">[:<remote branch>]
Branching and merging
# show existing branches $ git branch # create and step into the new branch $ git branch <new branch name> $ git checkout <branch name> # merge current branch with a specified branch $ git merge <branch to merge with> # deleting a branch $ git branch --delete <branch name>
Stashing
# ... hack hack hack ... $ git stash # make emergency fix $ git commit -a -m "Fix in a hurry" $ git stash pop # ... continue hacking ...